To make money in trading, you need to predict the price movement. Many traders use technical analysis to study patterns from the past to predict the future of the currency. Sadly, this is not always right and requires a lot of effort on behalf of the trader.
So, if a trader could make a wish, this will probably be time travel to see the future and then come back to its time and make the right call.
No one can see the future, but sometimes there are some delays in the market from which traders can take advantage. The person who applies arbitrage lives in the present and knows where the currency’s price is right to know. The forex market’s decentralized nature and its inefficiencies make it possible for a trader to “go back in time” and buy or sell a currency with a previous quotation and earn money.
What is arbitrage?
Arbitrage is an old strategy primarily used in the futures market. It is a set of trading strategies that seek to profit with no risk by trading between periods where a part of the market has not updated its price levels. Today, electronic operations reduced big-time arbitrage operations. Nevertheless, information can only travel as fast as the speed of light, so technically, there is a limit for information transmission. As a result, there may be a delay when updating prices for currencies.
Let’s explain with a simple example using the principle of arbitrage. Imagine that you were a gamer back in 2013. You played a game and earned one Bitcoin. Since then, you forgot about the game and never played again. The last time you heard about Bitcoin was years ago, and you heard that its value was around $1.000.
It’s 2021, and now someone offers you $1000 for your Bitcoin, and you accept. A few days later, you find out that Bitcoin is close to $50,000, but you already made the deal. The person who bought your Bitcoin applied for arbitrage and earned almost $49.000.
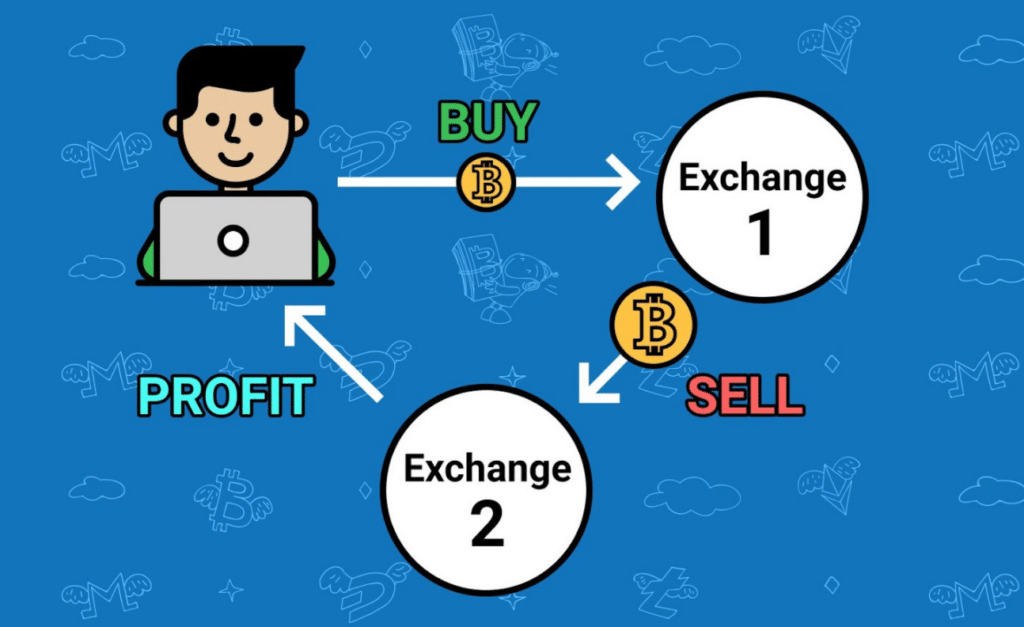
It took you to get the information about the current price of Bitcoin as the window of opportunity to apply arbitrage. But, of course, this doesn’t happen in real life. Everybody knows how much Bitcoin costs, but it is a simple way of looking at arbitrage. The previous owner of the Bitcoin lived in the past concerning the currency’s value, and the trader who bought the Bitcoin for $1000 didn’t risk anything because he already knows the current price.
How to apply arbitrage?
There are three main ways of applying arbitrage:
- Triangular arbitrage
- Interest rate arbitrage
- Statistical arbitrage
Triangular arbitrage
This type of arbitrage involves three currencies to complete the operation and make a profit. Let’s see how it works. Currencies are always compared to other currencies, and the relations between any pair of currencies should be equivalent.
Triangular trading seeks to make a profit from currency discrepancies. We can define the price of a pair by using a third currency as a parameter. This way, the pair we are interested in will be defined with a third currency. If the actual quotation of the pair is not the quotation obtained by comparing each currency against the third one, there is a discrepancy from which a trader can make money.
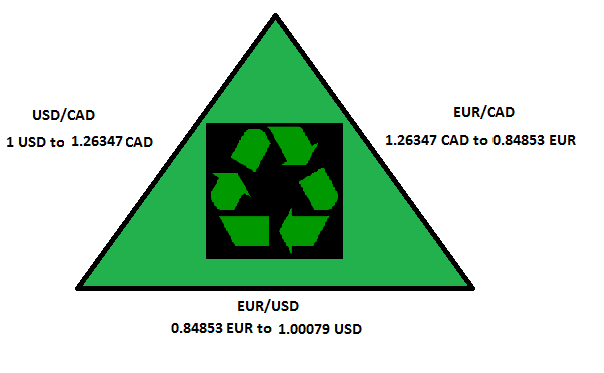
For example, let’s compare the pair formed by the USD, EUR, and AUD. Now, we will see if the price of the USD/CAD is right in terms of the other two pairs. For that, we look at the price of all the pairs.
- EUR/USD 1.17944
- USD/CAD 1.26347
- EUR/CAD 1.48900
To define the price of the pair, we can divide the other two pairs like this.
USD/CAD=EUR/CADEUR/USD=1.489001.17944=1,26246
So, we can see a difference between the current price of 1.26187 and the expected price of 1.26246. The discrepancy opens a window to buy cheaper CAD.
This way, the trade would go:
- The trader buys 1,26347 CAD in exchange for 1 USD (EUR/USD 1.17944)
- Then he trades his 1.26347 CAD for 0,84853 (USD/CAD 1.26347)
- Finally, he returns to the USD by selling his 0,84853 for 1,00079 USD (EUR/CAD 1.48900)
Statistical arbitrage
This arbitrage is based on the intrinsic value of the currency. Institutions have developed indexes that help them estimate the value of a currency in terms of their purchasing power. These indexes are related to the shape of the economy in general. Some important indexes are the purchasing power parity and the Big Mac index.
Using this, we can bet on which currency is undervalued and which one is overvalued. The problem with this type of arbitrage is that often it takes more time to make a profit and that time also represents a risk. The country’s condition could change before the market value meets the expected value, and the pair price may never meet the expected price level.
Interest arbitrage
It is also called carry trading. This strategy consists of selling a currency with low-interest rates to a currency with higher interest rates. This way, the trader makes more money because of the interest generated. However, there is an obvious downside to this. The currency with higher interest rates is probably more unstable and more likely to depreciate.
Central Banks use high-interest rates to motivate investors to use the country’s currency, which is not as attractive as other traditional currencies. Therefore, if the currency bought depreciates, we could lose more money than we planned to make. That is why this strategy has one more step. After you buy the quoted currency, you must purchase a put option, so in case the currency’s price drops, you can save your investment.

Risks
- For triangle arbitrage
The operational window is tiny, you have to execute the trades simultaneously, and the market can update the price level before you complete the operation.
- For statistical arbitrage
Time plays against you. When a currency is undervalued or overvalued, the correction takes sometimes. However, before both prices converge, the economic situation may turn around and change the intrinsic value instead of the market value.
- For interest rates interest
The value of the quoted currency may fall and make you lose money.
Disadvantages
- To get a decent reward, the size of the trade should be big.
- The opportunities for applying triangle arbitrage are scarce and close quickly. Moreover, it requires big hardware and software investment to do it.
Advantages
Low risks
People like to say that this is a risk-free strategy. However, depending on the type of arbitrage strategy you use, you may face certain risks. So, although it is not risk-free, it is a very low-risk strategy.
Final thoughts
In some ways, the triangle arbitrage strategy is still a dream for retail traders. The speed needed to perform the operations required a big investment in equipment and software. Triangle arbitrage is only for institutional traders that can afford the cost of the operations.
For the retail trader, the best options are statistical and interest rate arbitrage. These options have more risks, but also the reward is higher and can be performed by retail traders.