If you are thinking of investing in options trading, this article is for you. Options trading is becoming attractive to investors and traders as it hit a record high in the past year. According to the OCC (Options Clearing Corporations), options trading increased by 52.4% in 2020 compared to the previous year’s info. Both novice and professional traders embrace option trading and contribute to this sector’s growth.
However, options trading involves a different level of complexity and risk. So it requires understanding the total concept and following particular methods to make profits by investing in Fidelity options. This article will introduce you to option trading alongside explaining Fidelity options trading methods.
What is a Fidelity options trading strategy?
Such trading is a bit more complex than traditional CFDs or stock, which allows you to buy/sell ETFs, stocks, etc., at a particular price within a specific period. You also have the flexibility to purchase any security on a particular date or price. This type of investment allows making a significant profit as you don’t need to pay the total amount for any option contact of securities. It also protects your losses if the security price goes down in that period of contact, which is also hedging. The “Call” option gives you the right to buy, and the “Put” option gives you the right to sell.
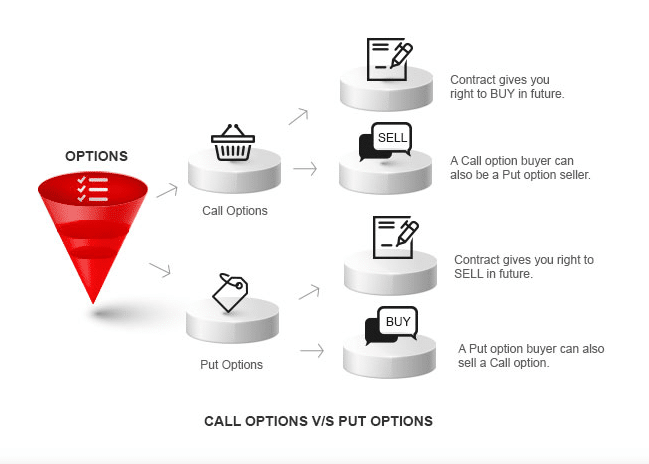
The seller is the “option writer” and has no right to hold; he must sell the security if the buyer chooses to buy the particular asset at the agreed price on the due date in exchange for an upfront payment from the buyer.
There is usually no physical document of the contacts when you enter into an option contract. The mandatory options trading terms involve European and American options, open interest, strike price, strike price intervals, lot size, and date expiration.
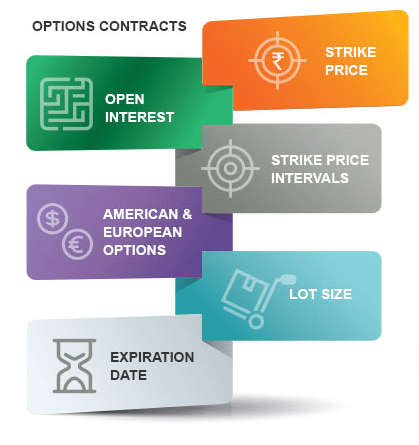
Premium
It is the payment that buyers pay to sellers to enjoy privileges of any options contract.
Strike price
The predefined price of the options contract, at which buy/sell occurs.
Strike price intervals
There are different strike prices for any options contract; the exchange defines these prices. The exchange declares nearly eleven prices for any options contract every month.
Open interest
It refers to the whole number of unique positions on any specific options contract across total participants in the marketplace on any particular period. It becomes nil past the expiration date for any particular contract.
Expiration date
A future date from the starting period of the option contract that on or before the contract will be executed.
Three different durations you can pick:
- Near month (one month)
- Middle month (two months)
- Far month (three months)
Many trading strategies are available to make money by investing in fidelity options contracts; each is a fidelity option contract strategy.
How to trade with Fidelity options contract trading strategy?
The strategy may be complex, but it allows anyone to profit with some easily applicable methods. The leading options trading platforms are.
| TD Ameritrade | Best overall options trading platform and tools |
| Interactive brokers | Best platforms for professional options traders. |
| Fidelity | The best platform for beginners. |
| TradeStation | The best options platform technology. |
| E*TRADE | The best web-based platform for options trading. |
Fidelity offers investments in fractional shares, forex, futures, retirement services, etc. It is a value-driven brokerage platform that provides excellent trading tools, leading research, an easy-to-use mobile app, and extensive retirement services. This platform is serving over 40 million users across the globe. It is a winning platform for frequent trading, and novice traders are comfortable with it.
Bullish setup/ Call options
For a better understanding of call options, look at the picture below.

It means Rajesh has the right to buy one lot of 100 Infosys shares anytime between now and the month of May at Rs. 3000 per share. He pays a total of Rs. 25000 for the right to sell where each share costs him a premium of Rs. 250.
Now suppose the price of Infosys shares rises to Rs. 3200 from Rs. 3000. Rajesh can exercise a buy options contract that shares Rs. 3000 and make a tentative profit by saving Rs. 200 per share. However, he is at a loss of Rs. 50 per share when you consider the premium he pays. So Rajesh may choose to exercise to buy when the price reaches Rs. 3250 or let the contract expire.
Bearish setup/Put options
Mr. Smith may think the ABC company has shares P that is overpriced. So he places a put option for a thousand shares at P at a strike price of 570$. So the total premium he pays is 1000X30=30,000$.
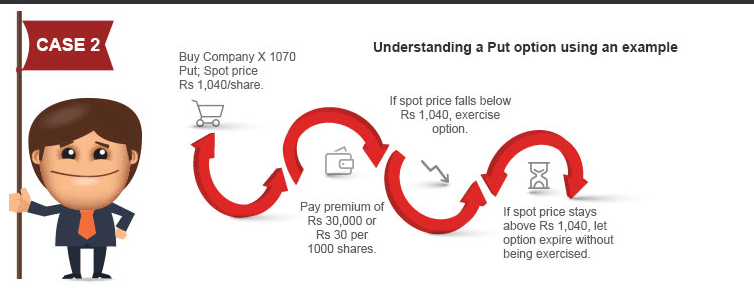
Suppose the price of P may fall at 520$, below the strike price. He can sell the put option to safeguard his investment. So he makes 50$ (570$-520$) per share, and a (50X1000=50,000-30,000(premium)=20,000$ net profit due to expiration date.
On the other hand, the price of P may increase to 580$. He will face loss if he exercises the put option at 570$. So if he doesn’t choose to exercise the put option, then he loses 30,000$-the premium, which is lower than the amount for losing if he exercises a put option.
Pricing procedure of an option contract
Buyers pay the premium to the sellers at a specific price, which is the entering price of an option contract. Three basic scenarios of trading in options are.
| In-the-money | You will make a profit by exercising the option contract. |
| Out-of-the-money | You will make no money by exercising the option contract. |
| At the money | No loss scenario, making a profit by exercising the option contract. You can consider the “in the money” as a call option when the strike price is lower than the spot price. |
Final thought
Many other trading strategies are available, such as covered call, married call, bull call spread, bear put spread, protective collar, long straddle, etc. You can choose any one of them to practice options contract trading. We recommend using any method only after mastering the entire concept, without any confusion.