You do not have to be a mathematician or statistic expert to understand the use of correlation in swing trading in practical terms. It is a robust measure in statistics that assists you in determining how movement in one currency pair mirrors the movement in other pairs.
What is a correlation in forex?
The FX market is among the dynamic, multifaceted asset platforms in the world. Being a currency trader, if you want to survive or thrive on this platform, understanding currency market strategies is necessary. A key dynamic in FX swing trading is “currency correlation.” As there are 73 different currencies available to trade in the FX market, each is correlated to some extent.
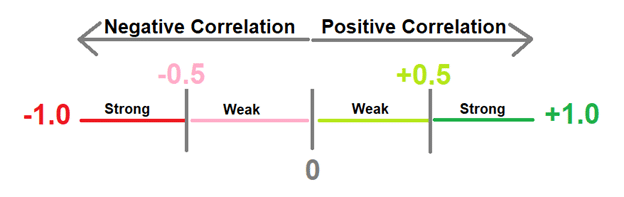
Here in the given figure, you can see the correlation illustration that there are two types:
- Positive
- Negative
For example, if two currency pairs have similar movements, you can directly correlate. It lies somewhere between 0 and 1.
On the other hand, if two currency pairs move in the opposite direction, they will predict an inverse correlation. The number of their correlations lies somewhere between -1 and 0 at the correlation illustration line. A strong positive correlation exists when the number lies above the +0.70 at the number line, while a strong inverse relation is present if the number lies below -0.70.
But, different instruments found on other asset classes have a severe impact on the currency movements and are still correlated with currency movement. So, if you learn the usage of correlation in swing trading, you will perform much better in the trading markets like FX.
You can identify inter-market moves and reduce the risk that will lead you to trade effectively. So, now the question is how to use correlation effectively in swing trading and how it will benefit. You will get the answer to these below.
Using correlation in swing trading
Do you know you can use correlation in the most common swing trading strategy, i.e., long-short strategy? According to their estimate, the traders buy the assets that can move up and sell the risk moving down. Of course, the traders need to be more careful in using this strategy. So here comes correlation’s use. As in swing trading, traders may open a trade that doesn’t go in their favor.
For example, a trader will open trade to buy a currency pair, say GBP/USD. Also, the same trader opens a trade to sell other currency, i.e., EUR/GBP. Both of these currencies could prove to be profitable to some extent. But there is risk in having both as traders do not have a common ground on the GBP.
So, the trade wishes the GBP to strengthen for the first trade, while he will wish the opposite for the next trade. So, here the trader needs to understand the concepts of correlation to maximize profits in swing trading.
Most of you, when exposed to the word correlation, might link it to the inter-market analysis. Here are some examples of correlations that are usually used in swing trading.
- AUD and NZD are always positively correlated.
- Gold has an inverse correlation with USD, while it is directly correlated to silver.
- USD/CHF and EUR/USD have an inverse correlation.
- Similarly, stocks and bonds also have an inverse correlation.
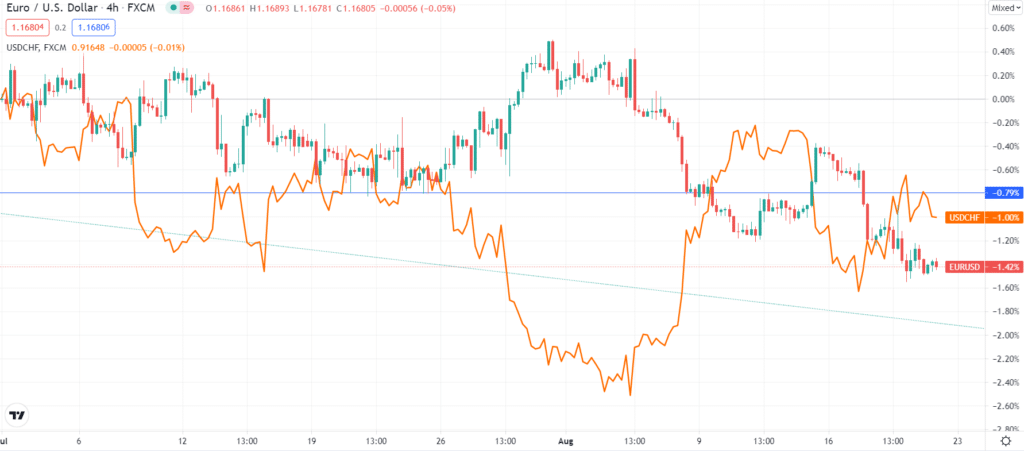
So, after understanding the use of correlation in swing trading, you should learn how to set up your correlation matrix.
Setting up your correlation matrix
The manual settings to determine a correlation matrix in MT 4 and MetaTrader 5 platforms are simpler and more accessible.
All you need is to follow the given steps:
Step 1. Select the currency pair that you want to correlate.
Step 2. Select the time frame that you usually use according to your trading style. As you are a swing trader, you might want to use the 4-hour time frame along with the 100-bar look-back period.
Note: if you are a medium to a long-term trader, you might use a daily time frame with a 25-bar look-back period. And if you are a day trader, you might go with a 10-minute time frame having a 100-bar look back period.
All of these are suggestions, and you can change them according to your trading strategy. The primary key is to select a perfect time frame and 100-bar look-back period that matches your trading style.
Step 3. The next step is to highlight the strong correlation that is visible on your screen. Then, you can quickly identify the currency pairs that are either moving intensely in lockstep or alternatively.
Step 4. You can analyze which market event has a similar impact on each currency pair. To make some of the heavy lifting easier, you can add custom indicators to your account. Now, here is another crucial point that is highly linked to correlation, i.e., divergence.
Trading divergence with correlation
In swing trading, you can use divergence to decide the entry and exit in a trade. The divergence mainly develops when the indicator is moving inversely to the actual price. So here is an example of silver and gold, which represent the use of correlation and divergence.
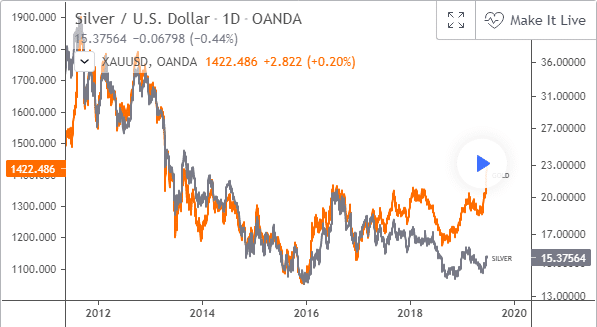
Here in the given chart, you can see that gold and silver are positively and strongly correlated. Therefore, this chart predicts that gold and silver both tend to move in the same direction. Now, we will see how divergence has an impact on it.
In this 30-minute chart, we find that silver and gold converge at the first part of the move. It represents that both metals are making higher highs and higher lows. Then, both metals start retracing, after which gold reaches a newer higher high and silver moves to another higher low.
Meanwhile, when gold gets a short-term top, the price starts to move sideways with silver. During this post redaction, the gold paid its divergence with a significant drop in silver. Thus, the zone coincides with the beginning of divergence between both commodities.
Final thoughts
Hence, the correlation in swing trading is the behavior presented by the currency pair that either moves in the same direction or is inverse. The swing traders pick up the time frame and look back period differently from the day traders according to their style. But having an understanding of correlation can save the swing traders from risks in the forex market.