Buying the underlying asset of an option is a smart decision if you are sure that it will rise in the future. With Leaps options, you can benefit from the rise of an asset without buying it and making even more money than those who own it.
While a simple Leaps options trade can make you earn 400%, 500%, or 600% of your investment, it would be fantastic if you could make even 70% profit with stock trading over a year. They are more investing than trading, and with much less money on the line, your reward and your probabilities are much higher than other types of options strategies.
Let’s check the keys to understanding Leaps options strategy.
How does the Leaps option strategy work?
Leaps is an acronym for “Long-term equity anticipation securities.” A Leaps option is one with an expiration date longer than a year after the option is bought or sold by the trader. So, they are options like any other but with an expiration date further away than the regular 30 or 60 days options.
Again, the Greeks play a crucial role here. The advantage of this strategy is to have a longer time frame for the asset to reach the strike price. Besides the fact that the longer time frame gives the trader more chance to hit the price, also, Theta is low in comparison. Thus, with the most options, the time is against the option buyer. But with Leaps options, time decay doesn’t impact the option price for most of the period. Only at the close of the expiration date does time decay strongly affect the options price.
Reason to use Leaps option strategy for traders
There are many reasons to use these options. Reward and winning probabilities are high, and there is plenty of time to adjust your trading if it goes against you. But without a doubt, the most attractive feature is the reward/risk ratio compared to the underlying asset. Let’s put an example.
There is this stock XYZ over which two traders are bullish. The price of the share is $251, and the first traders decide to buy 100 shares. The other trader buys a call option over one contract @ $265 instead.
The expiration date is a year away from the purchase of the Leaps options. Call options cost $2.88 per share, so the net cost is $200. A year later, the stock price was $19. The table below shows the performance of each trade.
| Trader | Initial stock price | Premium | Initial investment | Strike price | Break even price | Final price | Profit | % Profit |
| Stock buyer | $251 | N/A | $25,100.00 | N/A | $25,100.00 | $285.63 | $3,463.00 | 13.80% |
| Option buyer | $251 | $13.00 | $1,300.00 | $260.00 | $273.00 | $285.63 | $1,263.00 | 97.15% |
So, as we can see, the total amount of money is bigger on the stock’s buyer side, but every trader knows that the important thing is the risk/reward ratio.
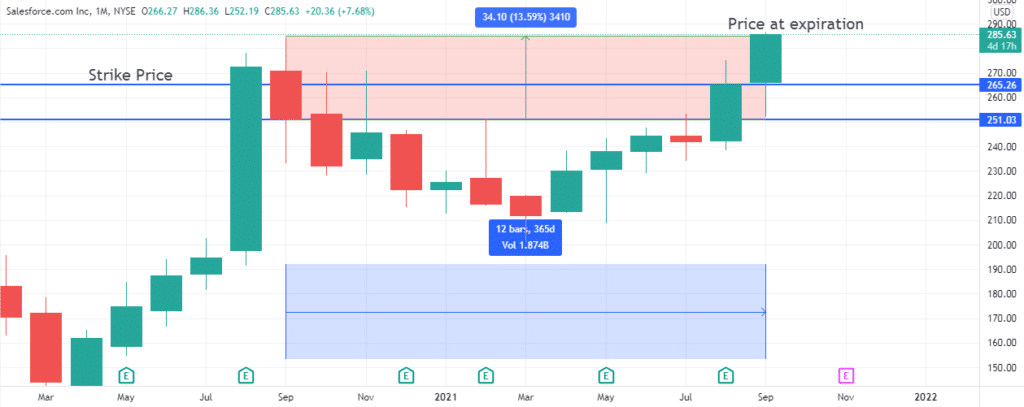
While the stock buyer risked $25,100 to earn $3,463 (13.00% profit), the option buyer invested $1,300 to make $1,263 (97.15%).
How to use the Leaps options strategy?
So far, the strategy sounds profitable and straightforward. It’s just a matter of making the option trade and waiting. But a good trader should know better. If it were that easy, everybody would do it. There are risks involved and, to avoid losing your gains, there are some conditions to look for when setting the trade. Let’s see which those conditions are:
1. Choose a good asset
The advantage of this strategy is the long time frame, but you still have to be confident the asset will be on the right level. Also, by buying not very popular options, as the volume will be low, the spread between the ask and bid price could be considerable, which could go against you whenever you want to exit the trade.
2. Look for a good delta
You want the closest thing to a delta = 1. That means that for every $1 the asset price rises, the option will increase too. Of course, you won’t find it, but everything above 0.8 it’s ok.
3. Set strike price at least 20% in the money
This will give you a better delta. Although, it will also increase the premium you have to pay.
Bullish trends
If you are bullish in the long term, the setup consists of buying call options so, with time, the price reaches your strike price, passes the break-even point, and starts giving you money.
Where to enter?
You want to enter your position on assets with high volume and delta above 0.80%. Since the time frame is very long, it doesn’t matter what the price is doing at the precise moment you buy the call option. What matters is the long-term trend. You want to bet on assets trending up in the weekly and monthly charts.
Where to put the stop-loss?
Again, the time frame is the key here. Since it is very long, there is plenty of time for the price to recover from a downtrend, so your risk tolerance should be higher. Nevertheless, we recommend a stop-loss 50% below.
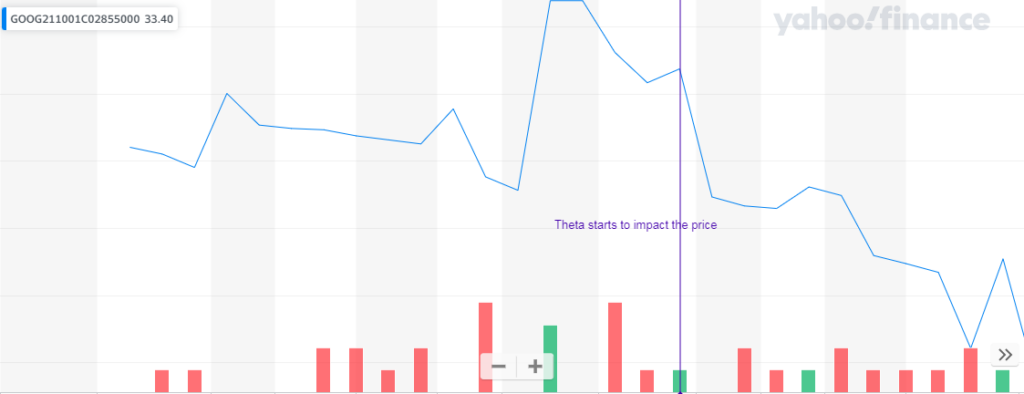
Where to take profit?
The margins we saw in the example are for investors that will hold options and execute them. For traders who won’t wait until expiration or strike price, a 50% gain is a decent target.
Bearish trends
If your sentiment is bearish, you want to buy put options because you are betting that the price won’t reach the higher strike price.
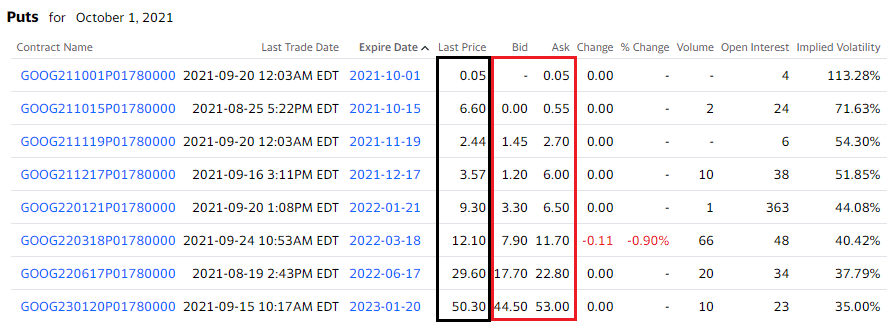
Where to enter?
Again, the trader is interested in the long-term trend rather than in the momentary trend. Therefore, you must look for a good delta and high volume.
Where to put the stop-loss?
The time left until expiration is very important. For example, if the price is down 25% nine months before expiration, it is not as big a deal as three months before expiration. Nevertheless, we recommend a stop-loss 50% below as a general rule.
Where to put the profit?
Place the take profit at 50% above the entry price.
Pros & cons
| •High reward When the trade goes right, you make more than you could by just buying the underlying. | •Time decay Even when the Theta impacts lower the price initially, like with any other option, close to the expiration date, the price will drop. |
| •Limited risk The risk of the trade is limited to the premium paid. This risk is also a lot less than they paid for the same amount of stocks. | •Implied volatility This is one of the factors that can affect the price of the option. |
| •High winning probabilities The long time frame makes it more likely that the underlying asset will hit the strike price. | •Bid/ask difference Because the expiration is so far away, there is not much volume. This generates a difference in the bid and the asked price of the option. If it is not managed correctly, it will create losses. |
Final thoughts
Leaps options are a great alternative to buy the underlying asset, whether we are talking about stocks, ETFs, or others. Like any other option, it allows us to leverage more significant amounts of assets with less money. The profits can be huge when it goes right, and the losses are always limited to the premium paid.