With after-hours trading, the investors can buy and sell stocks after the closing timings of the markets. The regular trading time of the New York Stock exchange and NASDAQ is from 9:30 am — 4 pm ET.
Such trading can be done in some brokerages even after the market closes. The advocates of this type of trade are fascinated with access to foreign market information and preferable timings according to their ease.
Starting your career as a stocks trader, you need to know when to trade without disturbing your regular schedule. So, in this article, we will discuss details of after-hours trading and which types of trades are restricted in those hours.
What is after-hours trading?
In this type of trading, a trader purchases or sells securities after the market closes. The standard time of the trading market is from 9:30 am to 4:00 pm Eastern time in both NYSE and NASDAQ. However, in the after-hours session, you can complete trades at any time between 4 pm-8 am ET.
By using electronic communication networks (ECN) for the extended hour’s sessions for trade, investors can match buyers and sellers without a traditional stock exchange. As a result, a relatively thin volume of financial deals takes place during this after-hour session. Due to the slow activity during these times, there are usually few active traders. However, there can be spikes in volume if big economic news breaks or a company makes a big announcement.
Limit orders (LMT)
One type of LMT is selling or purchasing an asset at a specific price or even better. It may or may not get filled according to market conditions and the price set by the dealer. If they are filled, the selling price will always be as expected. Sometimes it is even more than expected.
Using an LMT means you’re willing to go to great lengths to get a good deal, but you don’t care about the order being fulfilled. What is better depends on whether the deal is to buy or sell.
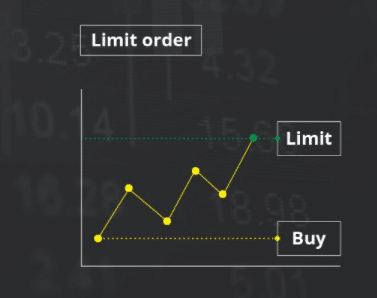
Traders placing LMT at $70.50 or less would only receive stock fillings if the stock could be purchased at that price. So unless you find someone willing to sell that stock for less than $70.50, your brokerage will not execute the trade.
You would place an LMT to sell a stock at $70.50 or more if you wished to sell the stock for at least that amount. You would not be able to execute the deal unless someone else offered you $70.50 for the stock.
Trailing stop orders
To set stop and stop-limit orders, the market price should be the basis for it, or at a specific price can be its foundation. Both stop and stop-limits can be set at a specific price or set concerning the market price. The term “trailing stop” describes a stop-limit order or trailing stop-limit that varies with the market price. These transactions protect investors’ profit margins.
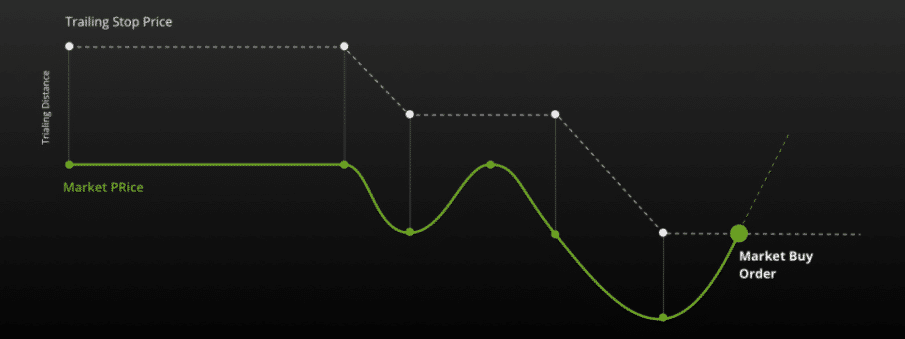
Suppose a trader bought a stock for $80. By the end of the week, the stock may have gone up to $83. In this case, the investor might set a trailing stop trade for sale at $2 below the market price. A trailing stop order to buy becomes a market order to sell the next day if the stock drops to $81, which locks in some profit for the trader. As a result, the trailing stop order trigger would become $83 if the stock price increased to $85 the next day.
According to market values, a dollar-cost or a percentage can determine the trigger price for trailing stop deals.
Stop-loss order
These are purchased or sold by a broker when a security reaches a specific price. These are designed to limit a security’s losses for an investor. An order becomes a market transaction when it falls below the stop price.
A trader can buy a stock and place a stop-loss deal 10% below the price of the stock. If the stock drops, it will be sold at market price, as the stop-loss order would be activated.
Which orders are not allowed in after-hours option trading?
It is noteworthy that investors may only place limit orders to buy and sell stocks in the after-hours session of markets. Orders are matched according to limit prices on the ECN. In addition, orders placed in such a way are valid only for that session. To buy the stock the following day, you will need to place another one when trading opens.
Main benefits of after-hours options trading
The popularity of odd-time investments among options investors is well-deserved. Among the advantages of post-session trading are:
Convenience
To place trades, you don’t have to hide at your desk from your boss.
Scheduling
Such trading allows you to react to the news without being constrained by regular trading hours.
Markdowns
- Such trading can be risky due to volatility; however, prices can be more attractive.
- Traders who trade after hours stay informed. Foreign market developments influence US prices directly in many cases, so knowing what is happening there is crucial.
Main risks of after-hours options trading
You encounter several risks when you trade after hours, even though there are numerous benefits:
Uncertainty in price
Fewer venues can be compared when a market closes. This could lead to the price being inaccurate in the upcoming regular session.
Reduced liquidity
Many times, you can’t trade your desired stocks during the after-hours trading session. However, due to low liquidity, trading costs can, unfortunately, increase.
Fill price is poor
Options traders may not have access to the best prices outside of market hours when trading outside of market hours. Therefore, trading after 4:00 reduces your chances of getting reasonable prices.
Final thoughts
Such a trading style is possible and can assist you in actively reacting to financial reports and several other market information outside of regular market hours. It’s essential to investigate each brokerage before committing to one, but each is a little different.