Industry and sector analysis in fundamentals is the keystone of various investment strategies. These analytical methods assist the investors in picking out productive and worthy stocks. A careful industrial analysis can unfold a company’s actual value, competitive ability, and dominance in a specific industry.
Financial services, real estate, and e-commerce are among the world’s biggest industries, having a market value of around 10 to 25 trillion dollars individually.
Resultantly, there is an augmented need for industry analysis to pick out the best stocks from these trillion dollars industries. So, do you want to know about the procedure and types of industry analysis?
Read this article to understand the industry analysis approach, its benefits, and various methods.
How does industry analysis work?
Industry analysis works by examining the nuances and dynamics of the relevant industry. It allows the companies and analysts to comprehend the detailed infrastructure of the industries and competitive pressure within a specific industry.
Moreover, through industry analysis, the analysts detect the pending threats or perils and upcoming opportunities regarding the on-focus domain.
Investors utilize this analysis technique for selecting stocks of companies with better positions and prospects in their sector. The in-depth industrial research and elaborate study before purchasing the investment products can enhance the winning chances.
Reasons to use for investors
Industry analysis makes it possible for investors to understand an arena’s intricacies and original framework. As a result, they refrain from making irrational and emotional decisions in a market panic.
Moreover, industry analysis is a fundamental analysis component that determines a security’s intrinsic value irrespective of price fluctuations and gauges the long-term outlook of the relevant companies.
In addition, it is a stable analytical method that allows investors to profit from the distinct characteristics of various companies. Furthermore, they can keep track of the continuously transforming environment of businesses and industries.
For example, Amazon Inc. is a leading company in the e-commerce industry with a market capitalization of above 1.5 trillion dollars. Most industry analysts consider this stock as an excellent investment option as the company has shown a remarkable competitive advantage in its industry.
How to use industry analysis?
Analysts and entrepreneurs mainly utilize three industry analysis methods for determining the profitability of an industry.
- Porter’s Five Forces of Competition framework
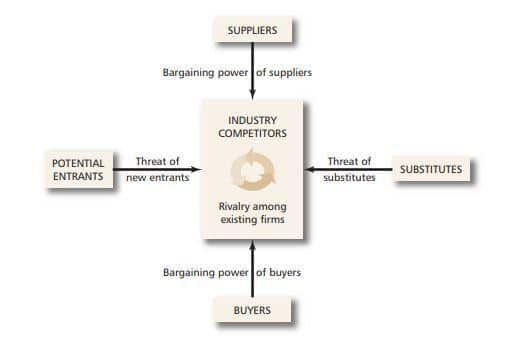
Michael Porter introduced this framework, in which he explained the five main competitive forces of industry. The central component of this model is the “rivalry among existing firms/companies” that can be in the form of aggressive competition or muted contests. Analysts study details like product differentiation, cost conditions, distinctions between competitors, and sellers concentration.
Moreover, the threat of new entrants and substitutes are the next two elements evaluated by investors. Competitors constantly face a threat of new & advanced firms settling in an industry if the entry barrier is low with higher profits probability. Analysts determine the position of firms in the competition and the chances of them getting substituted.
Furthermore, the last two constituents of Porter’s model are the bargaining power of suppliers and buyers. Estimating these bargaining powers can indicate the potential organizations with higher negotiation weightage and better quality services or products.
- SWOT analysis
It is a practical method that determines a company’s core strengths and weaknesses, projects and planning, performance, innovations, and risks. Analysts utilize various external and internal factors to compare and ascertain the companies’ future success chances.
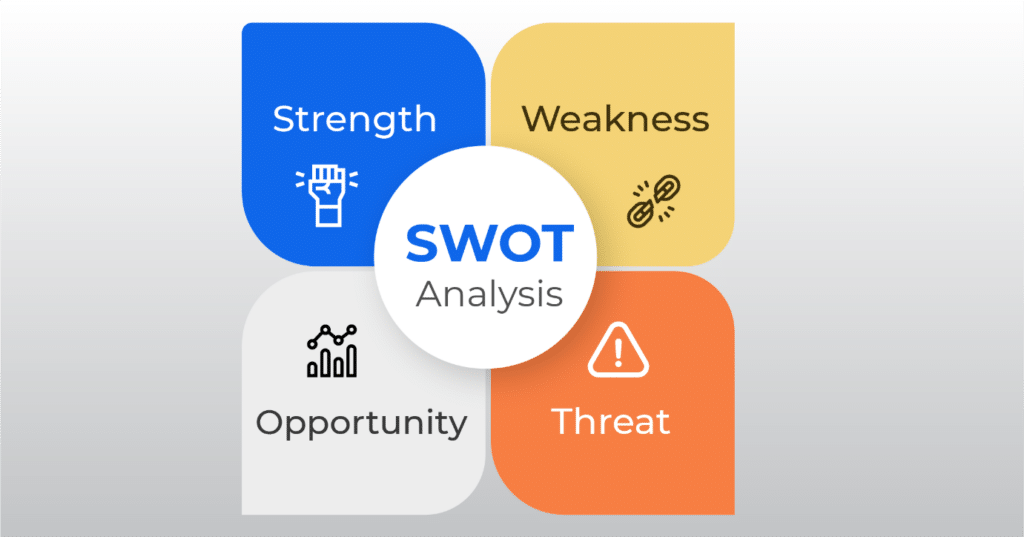
SWOT analysis involves the consideration of four key areas to establish the competitive position of the relative firms or corporations. They include:
- Strengths
- Weaknesses
- Opportunities
- Threats
Exploring these components can give a quick overview of the company’s standing. SWOT model can explain if a company is superior and dominant in its industry, its potential barriers or hindrances in performing good, its leadership power and capability to introduce initiatives, and the factors that can jeopardize its operations or functionality.
- PEST analysis
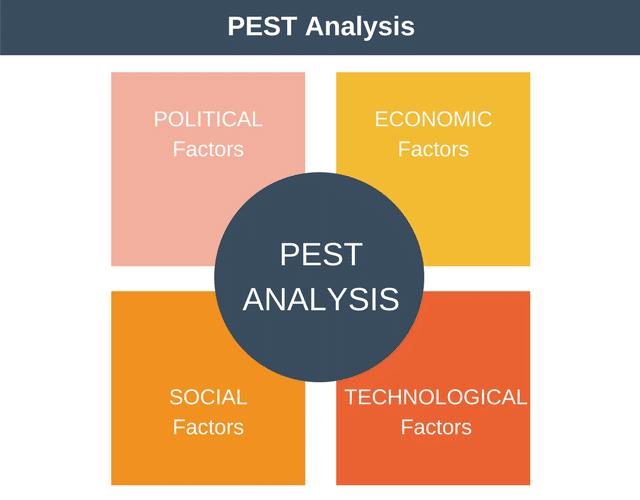
PEST analysis is a technique that assesses four external factors for establishing the competitive advantage and profitability of a specific organization/industry. The political component considers the government laws or regulations, tax laws, foreign policies, and the overall political system of a country.
The economic analysis sector examines the inflation pressure, supply and demand levels, GDP growth rate, and existing economic policies.
The social aspect deals with the study of social dynamics and cultural trends, whereas the technological analysis tracks the technological advancements and ongoing technological research related to an industry/sector.
Example of industry analysis stock
Here, we have discussed an example of a well-performing stock related to the financial services industry, selected by comprehensive industry analysis.
JP Morgan Chase & Co. is the leading US bank and the largest financial services company globally. It provides:
- Investment and deposit products.
- Payment solutions.
- Investment banking services.
- Lending & asset management services to consumers and businesses.
The bank has a stable and steady management framework and has shown consistent profitability data, making it an ideal investment option. The bank has a market capitalization of around 472 billion and a P/E ratio of 10.11. Moreover, it reported a gross profit (ttm) of 102 billion and earnings per share of $15.8.
The bank faced a hit at the start of pandemic turbulence; however, its intrinsic aptitude quickly set it on the path of recovery.
Pros & cons
Let us look at the advantages and limitations of industry analysis to pick out the best stocks.
| Pros | Cons |
| Independent of market panic Industry analysis does not consider the seasonal and temporary market sentiments, allowing the investors to remain steady in their positions. | Substantial expertise for research Industry analysis requires considerable skills and time-consuming research to select stocks. |
Establish the stability of a company Industry analysis points to the stocks with the most stability and sustainability, reducing the risk of losses. | Risk of incorrect interpretation It is a subjective analysis procedure, and every investor can conclude different results that can be wrong. |
| Prediction of long-term performance Industry analysis presents a long-term perspective of a company’s performance. Investors can engage in long-term investing by using this method. | Risk of new entrants Despite a detailed analysis before investing, the more developed and advanced entrants in an industry can disrupt the other businesses. |
Final thoughts
Industry analysis, which was initially the hallmark of only businesses and entrepreneurs, has now become an effective analytical tool among investors. Through this analysis technique, investors comprehensively study the nuances of companies within an industry and invest in firms with the best long-term potential.
Moreover, a correct analysis can provide investors with stable gains without constantly monitoring the price fluctuations. However, industry analysis is subject to wrong deductions as it is not an objective assessment method; hence investors should follow proper risk management and look out for any red flags.