Today, many acquisitions are occurring, which gives rise to the opportunity to use arbitrage strategies. The strategy can be advantageous if you choose the right merger.
The largest corporate merger, which occurred in February 2000, was between Vodafone and Mannesmann. Thus, the deal was worth roughly $183 billion. The agreement itself presented an excellent arbitrage opportunity for investors.
Seasoned investors have used arbitrage for many decades to their advantage. Warren Buffett famously used arbitrage from a young age, and it can also be one of the investment strategies you would want to make use of.
In this article, we will discuss merger arbitrage and the strategies to use to your advantage.
Understanding merger arbitrage
Arbitrage is the simultaneous buying and selling of the same asset when a price variation occurs. Merger arbitrage is one of three types of arbitrage investment strategies.
When an organization bids to acquire another company, it sells its stocks lower to existing stockholders. Therefore, stockholders can sell their existing shares at the current fair value and buy them at a discounted rate.
Usually, after a merger, a company’s stock price appreciates, and the shares you purchased at a lower rate have now gained in value. This is how you profit from merger arbitrage.
Types of merger arbitrage
A corporate merger can have two types, a cash merger, and a stock-for-stock merger. When a cash merger occurs, the acquiring corporation purchases the target company’s stocks in cash.
The stock-for-stock merger is when the acquiring corporation exchanges its stocks for the target company’s stocks.
An investor would buy the stocks of the target firm through a stock-for-stock merger. At the same time, they will sell the stocks of the acquiring company. The exchange of all assets of the target company occurs after the deal is closed. The investor will then use the exchanged stock to top up the selling position.
Arbitrage of cash mergers
During a cash merger, the corporation acquiring the shares has to announce the price they intend to buy the target company’s stocks. Investors who take advantage of the arbitrage have to rely on the success of the acquisition.
Let’s look at an example of a cash merger.
Company A is making an offer to acquire the stocks of Company B. The value of Company B’s stock is $70 a share.
Company A proposes to buy the shares at a higher rate of $150 per share in cash. They can afford to provide this discount price because the merger will bring added value to their company.
On the day of the deal’s news release, the value of Company B increases, and the price reaches $100 per share.
You see the opportunity for an arbitrage investment and decide to buy Company B’s shares. At $100 each. You have done your research on the merger and are confident that the deal will be closed.
Towards the end of the agreement, Company B’s share price rises until it reaches the $150 mark, which is the purchase price. Your profit in this instance would be $50 per share ($150 – $100).
There is a significant profit to make during cash mergers. However, this example is simplified, and in real life, you have to consider investment fees and taxes.
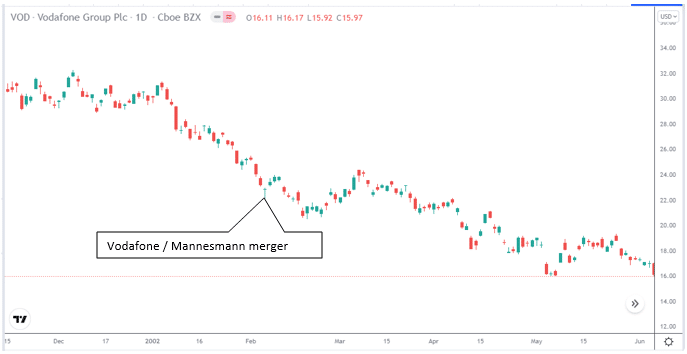
Vodafone merged with Mannesmann on 3 February 2002. It is still the largest acquisition in history.
Arbitrage of stock-for-stock mergers
An example of a stock-for-stock merger was the purchase of Postmates by Uber Technologies. Uber’s ride-hailing business suffered during the Covid-19 pandemic, and they relied mainly on the UberEats business to generate revenue. Postmates is a food delivery business. The deal was worth $2.65 billion, and the acquisition closed on 1 December 2020.
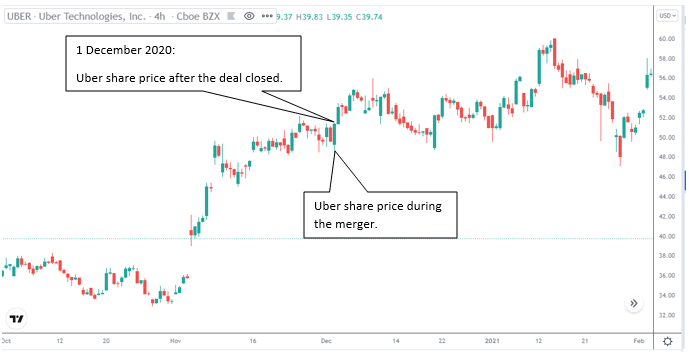
Uber’s share price during the merger. 1 December 2020, Uber’s share price increased after the deal closed.
There are two ways to benefit from this merger. You can take a short or long position by taking advantage of the stock price variance.
Bullish arbitrage strategy
Let’s see how you can benefit by following the bullish strategy. During the merger, Uber Technology was trading between $48 and $49 per share. This is the perfect time to buy more shares since the market anticipates the share price to increase after the merger.
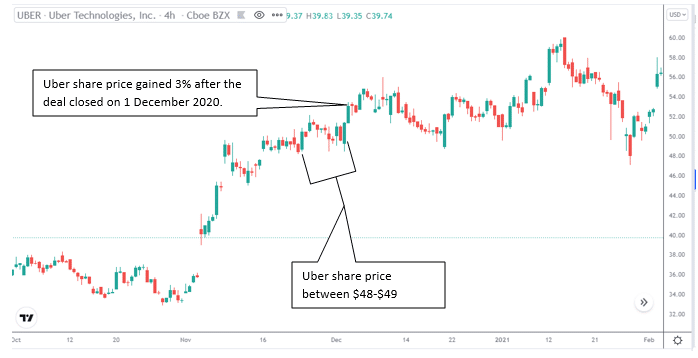
Furthermore, there was enough supporting information that the merger would be successful. The deal closed on 1 December 2020, and as predicted, Uber’s share price rallied to around $53.09 per share. This was an increase of almost 3% in one day.
Therefore, you would have made about 3% in profits if you had purchased at the $48 – $49 range.
Bearish arbitrage strategy
You can benefit from the same stock-for-stock deal by short selling. During the purchase, you can buy shares of the target company, in this case, Postmates. At the same time, you sell shares of Uber Technologies. As we see, once the deal was closed on 1 December, Uber’s share price increased by 3%.
This means that Postmates stocks go to Uber Technologies, and in this instance, the price would have increased as well. Now, you are holding Uber stocks, but your position has gained due to the Postmates stocks that you purchased. You now use the converted stocks to cover Uber’s stocks held in the short position.
Merger arbitrage risks
There have been many successful acquisitions in the past. However, there is some risk involved. There are a few factors that could prevent a successful acquisition.
- Regulatory risks
Deals have failed due to regulatory risks in the past. In some instances, the acquisition threatens the specific industry’s competitive nature or breaching a country’s regulatory conditions or laws.
- Over-priced premium
The premium price may be over-priced by the acquiring company. If you short the acquiring company’s stocks and the deal fails, the market will push the price further above the premium. You will be at a loss because you are holding sell positions of a stock increasing in value.
- Falling stock prices
The target company’s stock price might fall lower than during the merger, resulting in losses.
- Leverage risk
If you are using excessive leverage during a merger, the potential losses or profits can be significant. The risk comes in if the deal fails, which will result in higher losses due to leverage.
Pros & cons
We need to conduct due diligence by considering the pros and cons of merger arbitrage since, as an investor, you need to be aware of the risks and benefits that go along with merger arbitrage.
Pros | Cons |
| Almost risk-free investment Merger arbitrage comes with almost zero risks since you are betting on the success of the merger. | Risk of merger failure If the merger fails, you risk losing your investment and the positions you hold due to the arbitrage. |
Consistent profits You can make good consistent profits if you invest in good merger opportunities. | High leverage High leverage can cost you if the merger is not successful or if you have an insufficient margin. |
| Diversify Merger arbitrage is an excellent way to diversify your portfolio in the short term. | Capital gains taxes You have to pay taxes on your yields from the stock sales, and if you fail to make provision for this, it can diminish your profits. |
Final thoughts
Investing using arbitrage strategies is a powerful way to garner good profits. However, relying on stock mergers comes with inherent risks.
Acquisitions and mergers can fail, and investors should conduct thorough research into the companies involved in the deal. On the plus side, most mergers nowadays are between stable corporations, and these companies have sound growth, therefore lowering the arbitrage risk significantly.