Blockchain technology is reshaping the traditional world of centralized financial investment. Slower and more complicated transactions hinder individual investors’ ability to manage their assets or money. Protective and safe environments are provided in exchange for centralization.
In DeFi, formerly monopolized by governments and central banks, authority is shared among investors through consensus protocols, allowing them more control over their funds but simultaneously increasing the transaction speed and complexity. In addition, while giving complete transparency to all parties, DeFi automates trust and security.
In a short amount of time, the DeFi sector has grown worth billions of dollars. Since 2020, DeFi contracts have grown from $650 million to $43.50 billion in total value. Is this something you’d want to be a part of? Let’s keep on reading.
What is the DeFi yield farming method?
Putting crypto assets to work and maximizing returns on those assets is yields farming in its broadest context. A yield farmer may move assets around inside a compound in its most basic form, searching for the pool with the most profitable APY week after week. However, a yield farmer can cope with the danger of changing into more risky pools from time to time.
New price arbs [arbitrage] may arise due to farming, impacting other protocols whose tokens are in the pool. In contrast, they may go considerably farther since these positions are tokenized.
If a farmer wants to invest $100,000 USDT in the compound, they may do so. Those that invest will be given a cUSDT token. So, let’s assume that the compound formula gives them 100,000 cUSDT back (the formula is insane, so it’s not precisely 1:1).
They may then utilize Balancer, an AMM that allows users to build self-rebalancing crypto index funds, to deposit the cUSDT in a liquidity pool that accepts cUSDT. It might lead to a bit of increase in transaction costs in most cases. The foundation of yield farming is based on this idea. The user aims to maximize yield across as many products as possible by searching for edge cases in the system.
How to trade using the DeFi yield farming method?
Individuals who provide their cryptocurrencies to the DeFi platform’s functioning are liquidity providers (LPs). A decentralized application (dApp) using smart contracts called a liquidity pool keeps all of the money for these LPs. The DeFi platform that the liquidity pool is operated on pays LPs a fee or interest when they deposit tokens in the fund.
By lending your tokens to the decentralized software, you’ll be able to earn money (dApp). Moreover, since smart contracts are employed, there is no middleman or intermediary in the funding.
A marketplace for lending and borrowing tokens is built based on a liquidity pool. Liquidity providers are compensated for staking their tokens in the pool by charging fees on these markets.
Most yield farming occurs on the Ethereum platform. Therefore, the rewards are in the form of ERC-20 tokens. Loan providers have complete discretion over how their borrowers may use their tokens, but most are now speculators looking to benefit from the token’s price volatility.
Bullish trade setup
Let’s learn more about buying the stakes in yield farming.
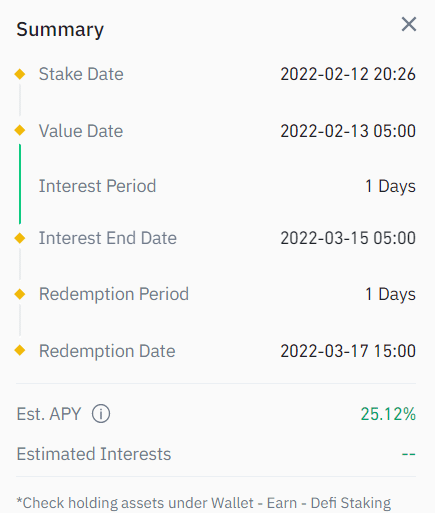
Entry
You can enter in staking at any point. However, the best point is when a new coin appears in the market as the APY (yielding rates) is relatively high. But, conversely, there is a considerable risk in such staking too. So, the wise decision is to enter yield farming when a new coin settles into a price range behavior.
Stop loss
Unlike trading, there is no stop-loss in yield farming. However, it would help if you exited the staking when the staking time is up or when you see a massive plummet in price.
Take profit
It is recommended to stake for a month, reap profit, and then stake the entire earnings again to compound profit.
Bearish trade setup
Now take a look at the bearish angle of yield farming.
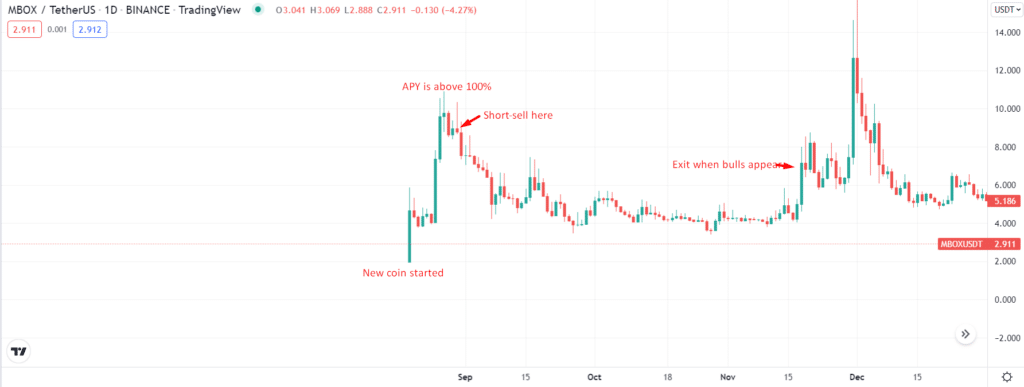
Entry
We know that the high-risk assets have higher APY (yielding rates). So, such projects are prone to a high drawdown in price. While staking, you can hedge your losses by short-selling such an asset in the futures market. Take a look at the above chart.
Stop loss
There is no stop-loss. Only invest an amount you can afford to lose. Use 5x or 10x leverage. Your investment amount is your stop-loss.
Take profit
Exit the trade in profit when you see strong bulls appearing. You can enter the short setup again when you see any bearish behavior.
How to make $500 per day with this strategy?
What happens if you have both an unpredictable loan and uncertain collateral? The market may turn against you with volatile assets and force you to sell your investments. Reduce the risk of liquidation by borrowing or providing less volatile assets. You should know your liquidation risk if you employ a collateralized loan via Compound, MakerDAO, or Aave.
A stablecoins like USDC or WBTC would be preferred as security for a loan. If the collateral and the loan are both less volatile assets or stablecoins, the chance of liquidation is significantly reduced.
In addition to earning tokens for giving or borrowing liquidity, some farmers may invest their cash in liquidity pools to generate yield. These pools, pioneered by Uniswap, let users receive trading fees from decentralized exchanges. As a result, customers may benefit from market-neutral returns, enabling them to reduce their portfolio’s volatility.
When it comes to freebies, there is none. Uniswap or other AMMs may be advantageous in certain situations, but if the price changes too much, you may end up losing money as opposed to holding the underlying assets yourself. This concept is referred to as Impermanent Loss.
They should also look at using protocols other than Unsiwap, such as Curve or Balancer, to avoid problems with impermanent loss by carefully selecting the pools they join.
Final thoughts
A developing technology that claims to do away with intermediaries in financial transactions, DeFi, has presented investors with many income sources. Investing in yield farming is an example of DeFi. Bitcoin and other cryptocurrency tokens may be loaned or staked in return for transaction fees, interest, or both. To put it another way, it’s like receiving interest from a bank account since you’re lending money. However, just-yield farming may be more difficult, riskier, and unpredictable than putting money in a bank.