Swing trading is an effective strategy that lets you profit by spending less time on the screen. You don’t need to glue yourself to the screen like day trading or scalping, and you don’t have to wait several months for the profits to come like position trading.
Just ask Alan Farley, who used swing trading as his trading style and became co-owner of CNBC. But, first, let us remind you that CNBC is watched by 84.27% of Americans who own TV.
The good thing about swing trading is it doesn’t bind you with certain indicators or time frames. You can choose any indicator or apply any filter to your swing trading strategy.
In this guide, we’ll mention the three best strategies to short SPY. These strategies will help you learn swing trading, and in the process, you can make $500 in ten minutes of trading.
Strategy 1. Put options
When talking about swing trading and profiting on the bearish market, put options can do the job.
The put options give you the right to sell 100 shares of a stock or any other asset at a certain price within the expiration date. This certain price refers to the strike price.
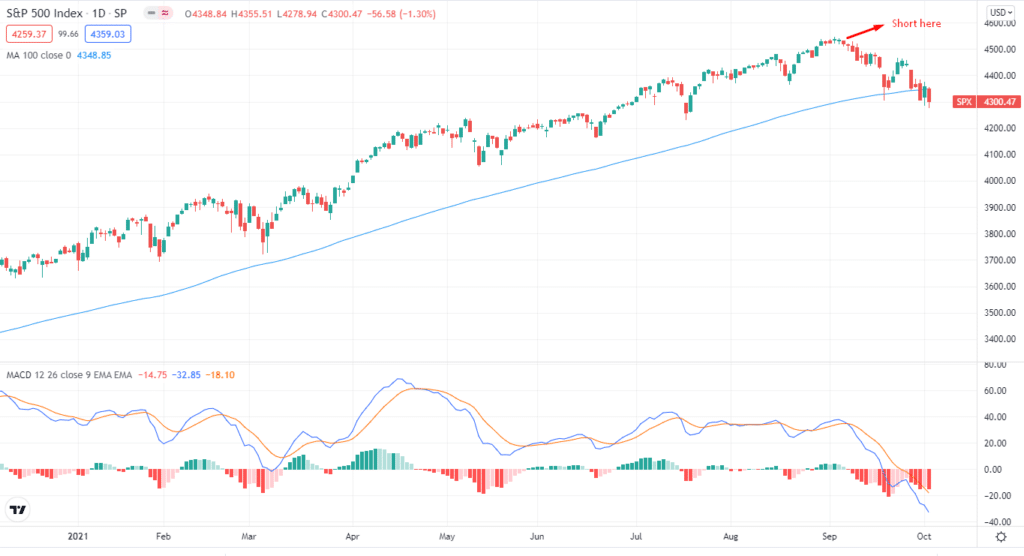
The put option becomes more meaningful when the price of a stock decreases. In this strategy, you expect SPY to go down, and you can make a short bet with the put option. On the other hand, when the price climbs, the put options strategy becomes unprofitable.
Let’s look at an example. Suppose you want to take a put option on SPY at a strike price of $100 with each share costing $4500 or $450,000 per contract, and you want to sell ten shares.
Depending on your trading account, you can sell ten shares for 450,000x ten = $450 0000, and you are making a deal on 10 x 100 = 1000 shares (as the options contract is 100 shares).
If the price drops to 10%, then the price will be $90, with a per-share price of $100 – $90 = $10 per share or $10,000 on 1000 shares.
A keynote to add here is you can’t exercise a put option before expiration. This means that you can close the position at a profit or a loss before the specified date.
Furthermore, the leverage of an option decreases the amount of money invested in a short position. One guideline is that if an option’s premium has lost half of its value, you should sell it because it will most likely expire worthlessly.
Strategy 2. Inverse S&P 500 Exchange Traded Funds
Inverse ETFs fluctuate in the opposite direction from their indexes. For example, an inverse ETF on the S&P 500 would use shorting and derivatives trading techniques to achieve the desired outcome.
In this technique, you borrow the asset from the broker and instantly sell the shares at the current market price, resulting in a short sale. Then you buy the shares back at a lower price, making a profit on the deal.
The good thing about inverse ETFs is that they do not require you to hold a margin account, as would be the case if you want to enter short positions normally.
A margin account is one where a broker lends you the money to trade. Margin is used with shorting as an advanced shorting method.
You enter into short positions and borrow the assets. You don’t own any of them so that you can sell them to other traders. Your goal is to repurchase the asset at a lower price and ease the trade by returning the shares to your broker.
However, there is a risk in this approach. If the asset’s value rises instead of falling, you have to repurchase the asset at a higher price than the original selling price.
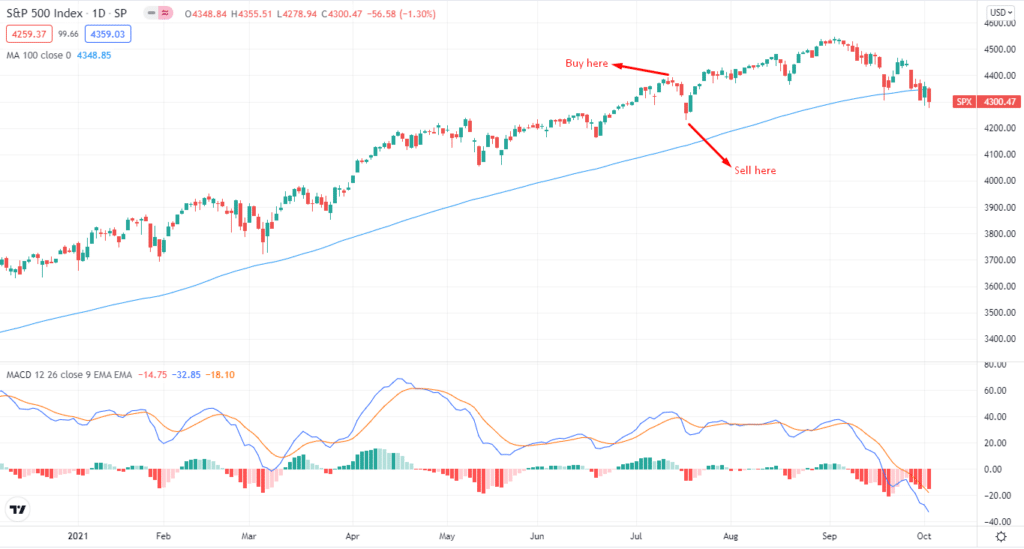
Let’s use an example to illustrate inverse ETFs strategy.
Suppose you want to take a short position on SPY. First, you’ll borrow the position from your broker and then sell it later to your broker as part of your swing trading.
You can also sell it in a day or two, but the market can go wild sometimes, so it’s good to keep your positions intact for at least one week.
Strategy 3. Inverse S&P 500 mutual funds
Like inverse ETFs, S&P 500 mutual funds, involved in the short-selling of assets included in the index. They also use derivative assets.
There are different ways to get around inverse mutual funds. For example, you can trade against the broader market by buying put options on SPY while shorting futures contracts on the index. The other strategy is the more common one. You need to short certain assets in the hope that the price will devalue.
Besides this, you can take positions on assets like gold and other safe-havens. These assets tend to gain value when the overall market dips.
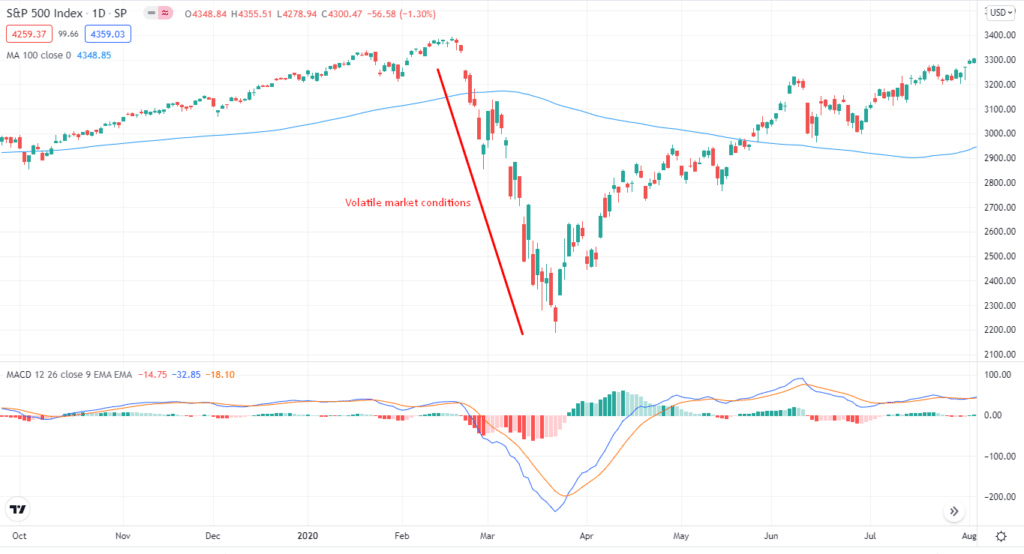
Note that when a trader applies an inverse mutual funds strategy, he/she is looking for excessive returns. You don’t have to be a genius to know what unreasonable returns are. They are those returns that you achieve beyond your proximity during volatile market conditions.
Of course, it depends on your investment and overall analysis, but you can make significant returns in a shorter time.
Let’s define an inverse mutual fund strategy with an example.
Suppose SPY is making wild swings; you would short your mutual funds’ positions and wait for the price action to continue trending downward. To exit the trade, you need to leave your positions when the market is still volatile. If the market starts to drift towards normality, you can lose big.
Pros & cons
Now that you know the three best strategies to short SPY, let’s discuss their pros and cons.
| Pros | Cons |
| •In swing trading, it is better to bet against the market instead of blindly following it. •When applied, all these strategies can bring in significant profits. • Because of the market’s historical upward movements, swing trading seems a viable option for shorting. | •Even in the best-case scenario, you can’t time the market. • It’s hard to identify which assets to short sell. |